FOURTH INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION
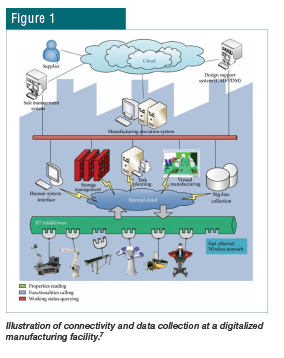
 | The Fourth Industrial Revolution (Industry 4.0) is the ongoing transformation of traditional manufacturing and industrial practices combined with the latest smart technology.1 Digitalization, smart manufacturing, as well as a few other terms all relate to Industry 4.0. At its core, Industry 4.0 makes use of digital technologies to improve business. This means business and manufacturing information (data) that is natively digital or digitized can come together and be used to solve complex business challenges. Industry 4.0 includes many subcomponents such as big data, artificial intelligence and additive manufacturing. When each subcomponent is examined individually, it is apparent that data collection and analysis is a key feature of Industry 4.0 operations. This article will discuss a few key segments of technologies within Industry 4.0 such as Internet of Things (IoT), autonomous robotics, data collection, big data and cloud computing. ADDITIVE MANUFACTURINGAdditive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, references the process of creating physical objects through the layering of melted or semi-melted substrate. Common substrates are polymers, composites, metals, ceramics and edible materials. Computer-aided design (CAD) software is utilized to design three-dimensional objects that can then be manufactured. Advancements in additive manufacturing have created many advantages within industrial market segments, including the rapid design and prototyping of equipment and maintenance-related parts. ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE/MACHINE LEARNING Artificial intelligence is a subset of computer science that focuses on the development of systems that can mimic certain human behaviors, such as learning and problem-solving. The advancement of computing systems in the 21st century has enabled the development of systems that can handle much more complex algorithms in much less time. Utilizing machine-learning algorithms, a corporation can now perform tasks that were once unfathomable. A corporation can now easily predict when a bearing will fail on a piece of equipment, identify which customers will potentially leave within the next quarter and hire employees based on their likelihood to succeed within the organization. AGUMENTED REALITYAugmented reality is an interactive experience between the real world and overlaid computer-generated sensory information. This information could be in the form of visual aids, audible queues or even haptic, somatosensory and olfactory forms. Through the implementation of an augmented reality headset, a production worker would not only be able to see and perform their job as usual, but also see additional information about the equipment or process displayed over the task. AUTONOMOUS ROBOTICSAutonomous robots, also known as autorobots or autobots, perform tasks without external influences. The key components and criteria for a robot to be considered autonomous include self-maintenance, sensing the environment, task performance and autonomous navigation. With the implementation of autonomous robotics, corporations can remove process variability while decreasing the need for human interaction related to dangerous tasks. DATA COLLECTIONImplementing data collection across the manufacturing space creates the need for robust data storage solutions. Three common local/on-premises data storage architectures include server-attached storage, network-attached storage and storage area networks.4 There also exist many off-premises options for storing data in the cloud. Choosing the right data storage architecture is directly influenced by the needs and resources of the organization and required reliability and performance needs. Additionally, organizations must find a solution that balances optimal performance with budgetary restraints. BIG DATA/BIG DATA ANALYSISBig data is data that contains greater variety arriving in increasing volumes and with ever-higher velocity. This is known as the three Vs.10 With recent developments in data storage solutions, corporations can now store much more data at a substantially lower cost. The availability of substantially more data allows for richer data analysis and the ability to confirm data veracity. By leveraging the ability to analyze big data, corporations can confidently gain operational insights and implement change. CLOUD COMPUTINGCloud computing is the on-demand online availability of computer resources such as data storage, computational processing and software. Cloud services rely on shared resources and economies of scale to provide a pay-as-you-go service for corporations. Through the utilization of cloud computing, corporations can access data, computational resources and software at an advanced rate while keeping setup and maintenance costs minimal.
| ||
AUTHORS | |||
| Sam Matson | ||